1 概述
定义:定义一组算法,将每个算法都封装起来,并可以互换。通用类图如下:
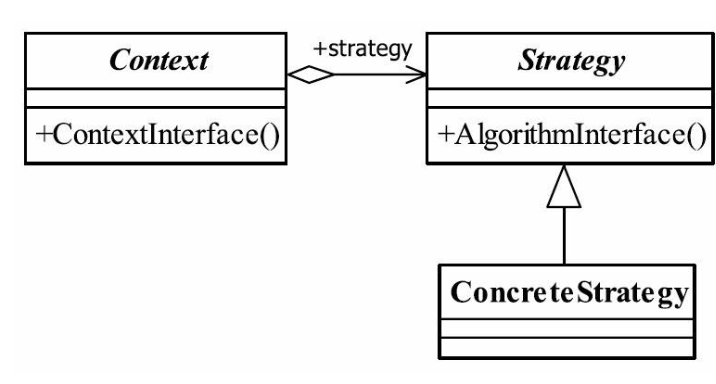
策略模式使用的就是面向对象的继承和多态机制,非常容易理解,主要有三个角色:
strategy:策略接口,定义每个策略或算法必须有的方法和属性。
context:上下文角色,主要作用是屏蔽高层模块对策略的直接访问
concreteStratety:具体的算法或策略。
2 代码示例
2.1 通过手动初始化策略集合
定义一个接口,再写两个实现类
/**
* @author chiangtaol
* @date 2020-12-05
* @describe 策略抽象类
*/
public interface StrategyAbstract {
/**
* 每个策略对应的类型
* @return /
*/
int getType();
/**
* 每个策略要做的事情
*/
void doSomething();
}
/**
* @author chiangtaol
* @date 2020-12-05
* @describe 策略1
*/
@Component
public class Strategy1 implements StrategyAbstract{
private final int type = 1;
/**
* 每个策略对应的类型
*
* @return /
*/
@Override
public int getType() {
return this.type;
}
/**
* 每个策略要做的事情
*/
@Override
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println("策略1方法执行...");
}
}
/**
* @author chiangtaol
* @date 2020-12-05
* @describe 策略2
*/
@Component
public class Strategy2 implements StrategyAbstract{
private final int type = 2;
/**
* 每个策略对应的类型
*
* @return /
*/
@Override
public int getType() {
return this.type;
}
/**
* 每个策略要做的事情
*/
@Override
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println("策略2方法执行...");
}
}创建一个封装了策略调用的类
/**
* @author chiangtaol
* @date 2020-12-05
* @describe 初始化策略集合
*/
@Component
public class StrategyContext implements ApplicationContextAware {
private Map<Integer,StrategyAbstract> map = new HashMap<>();
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
Map<String, StrategyAbstract> result = applicationContext.getBeansOfType(StrategyAbstract.class);
System.out.println(result.entrySet().size());
result.values().stream().forEach(e->this.map.put(e.getType(),e));
}
public Map<Integer, StrategyAbstract> getMap() {
return map;
}
/**
* 调用算法
* @param type
*/
public void doSomething(int type){
map.get(type).doSomething();
}
}调用策略算法时,直接获取context类,传入业务类型,这里使用的是策略类中type字段,根据不同type获取不同实现类,从而免去了if-else。
@Resource
private StrategyContext context;
@Test
public void test(){
context.doSomething(2);
}2.2 通过spring管理自动获取策略集合
每个策略在使用@Component时指定唯一的名称
@Component("s1")
public class Strategy1 implements StrategyAbstract{
private final int type = 1;
/**
* 每个策略对应的类型
*
* @return /
*/
@Override
public int getType() {
return this.type;
}
/**
* 每个策略要做的事情
*/
@Override
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println("策略1方法执行...");
}
}
@Component("s2")
public class Strategy2 implements StrategyAbstract{
private final int type = 2;
/**
* 每个策略对应的类型
*
* @return /
*/
@Override
public int getType() {
return this.type;
}
/**
* 每个策略要做的事情
*/
@Override
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println("策略2方法执行...");
}
}在使用时可以直接获取策略Map,其中key为@Component("s2")的name属性
@SpringBootTest
class StrategyAbstractTest {
@Resource
private StrategyContext context;
@Resource
// 直接注入实现类Map
Map<String ,StrategyAbstract> abstractMap;
@Test
public void test(){
context.doSomething(2);
context.getMap().get(1).doSomething();
// 通过注入一个接口实现类map获取策略
abstractMap.get("s2").doSomething();
}
}